Many computer users do not pay attention to partition file system, others have heard about file system, but they do not know the detailed information about File System, especially, FAT and NTFS, so in this article I’ll explain what FAT file system and I’ll talk about other file system in the future.
What is FAT File System?
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system that was developed for MS-DOS and is the primary file system for consumer versions of Microsoft Windows up to and including Windows ME. The FAT file system is considered relatively uncomplicated, and because of that, it is a popular format for floppy disks; moreover, it is supported by virtually all existing operating systems for personal computers, and because of that, it is often used to share data between several operating systems booting on the same computer (a multi-boot environment). It is also used on solid-state memory cards and other similar devices. It has a serious drawback in that when files are deleted and new files written to the media, the files can become scattered over the entire media making reading and writing a slow process. De-fragmentation is one solution to this, but is often a lengthy process in itself and has to be repeated regularly to keep the FAT file system clean.
FAT12 File System
FAT is also called 12-bit FAT, the file allocation table (FAT) for a floppy disk. The location of files on a floppy disk is listed in a one-column table in the FAT. Because the width of each entry in a floppy disk column is 12 bits, the FAT is called FAT12. As a file system for floppy disks, it had a number of limitations: no support for hierarchical directories, cluster addresses were “only” 12-bits long (which made the code manipulating the FAT a bit tricky) and the disk size was stored as a 16-bit count of sectors, which limited the size to 32MB.
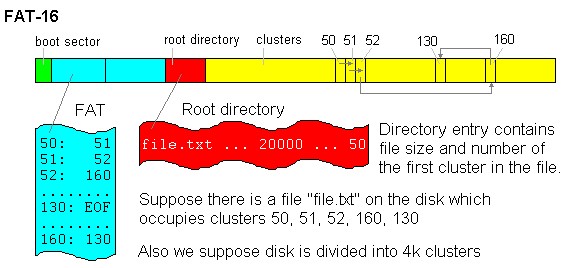
What is FAT16?
File allocation table that uses 16 bits for addressing clusters. Commonly used with DOS and Windows 95 systems.
A 16-bit DOS and Windows file system (see FAT) that varies cluster sizes based on hard drive size. Cluster sizes range from 4K (for drives up to 127MB), to 4K (255MB drives), 8K (511MB drives), 16K (1GB drives) and 32K (for drives up to 2GB). The ultimate capacity of a FAT16 partition is 2GB.
What is FAT32?
A disk file allocation system from Microsoft that uses 32-bit values for FAT entries instead of 16-bit values used by the original FAT system, enabling partition sizes up to 2TB (terabytes). FAT32 first appeared in Windows 95B and is also found in Windows 98 and Windows NT 5.0.
In order to overcome the volume size limit of FAT16 while still allowing memory-constrained DOS real-mode code to handle the format, Microsoft decided to implement a newer generation of FAT, known as FAT32, with 32-bit cluster numbers, of which 28 bits are currently used.
In theory, this should support a total of approximately 268,435,438 (< 228) clusters, allowing for drive sizes in the range of 2 terabytes. However, due to limitations in Microsoft’s scandisk utility, the FAT is not allowed to grow beyond 4,177,920 (< 224) clusters, placing the volume limit at 124.55 gigabytes, unless “scandisk” is not needed. Windows 2000 and XP placed a limit on the size of FAT32 partitions they can create at 32 GB, Microsoft says this is by design but does not explain why, and those versions of Windows are quite capable of reading and writing larger FAT32 partitions created by other means. FAT32 was introduced with Windows 95 OSR2. The many changes it incorporated made it a major improvement. However, by partition magic software, you can create 2TB FAT32 partition and overcome the 32 GB limitation in Disk Management.
The maximum possible file size for a FAT32 volume is 4 GB minus 1 byte (232-1 bytes). For most users, this has become the most nagging limit of FAT32 as of 2005, since video capture and editing applications can easily exceed this limit, as can the system swap file.
32-bit File Allocation Table File System Not the same as VFAT or FAT, which are both 16-bit file systems.
Please note that FAT12/16/32 is file system of a partition, there is another terminology named FAT, too. This is just part of FAT file system, besides FAT, there are other parts in FAT file system, which is MBR (Master Boot Record), DBR (DOS Boot Record), FDT (File Directory Table), Data zone. NTFS file system also contains MBR, DBR and Data zone. We’ll discuss these terminologies in the future.
Get what you need about hdd tool, pc utilities
