RAID Levels 0 1 (01) and 1 0 (10)
Common Name(s): RAID 0 1, 01, 0/1, “mirrored stripes”, “mirror of stripes”; RAID 1 0, 10, 1/0, “striped mirrors”, “stripe of mirrors”. Labels are often used incorrectly; verify the details of the implementation if the distinction between 0 1 and 1 0 is important to you.
Technique(s) Used: Mirroring and striping without parity.
Description: The most popular of the multiple RAID levels, RAID 01 and 10 combine the best features of striping and mirroring to yield large arrays with high performance in most uses and superior fault tolerance. RAID 01 is a mirrored configuration of two striped sets; RAID 10 is a stripe across a number of mirrored sets. RAID 10 and 01 have been increasing dramatically in popularity as hard disks become cheaper and the four drive minimum is legitimately seen as much less of an obstacle. RAID 10 provides better fault tolerance and rebuild performance than RAID 01. Both array types provide very good to excellent overall performance by combining the speed of RAID 0 with the redundancy of RAID 1 without requiring parity calculations.
RAID 10 VS RAID 01
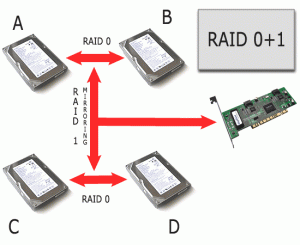
RAID 0 1 Combination of RAID 0 (data striping) and RAID 1 (mirroring). Optimize for Performance and Redundancy
RAID 0 1 combines the performance of RAID 0 with the redundancy of RAID 1.
To build a RAID 0 1 array, you first build a set of RAID 1 mirrored disks and you then combine these disk sets in a RAID 0 striped array.
A RAID 0 1 array can survive the loss of one disk from each mirrored pair. RAID 0 1 cannot survive the loss of two disks in the same mirrored pair.
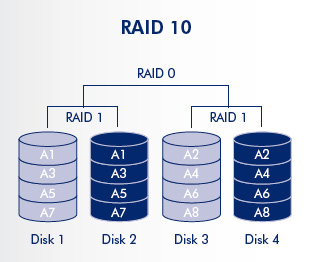
RAID 10 and RAID 01 are not the same thing and it does matter. RAID 01 is a mirrored configuration of two striped sets. RAID 10 is a stripe across a number of mirrored sets.
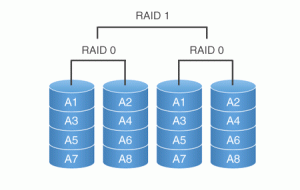
RAID 10 provides better fault resilience and “rebuild” performance than RAID 01. Both array types provide very good to excellent overall performance by combining the speed of RAID 0 with the redundancy of RAID 1 without requiring parity calculations.
- Minimum number of drives: 4
- Strengths: Highest performance, highest data protection (can tolerate multiple drive failures).
- Weaknesses: High redundancy cost overhead; Because all data is duplicated, twice the storage capacity is required; Requires minimum of four drives.
Controller Requirements: Almost all hardware controllers will support one or the other of RAID 10 or RAID 01, but often not both. Even low end cards will support this multiple level, usually RAID 01. High end cards may support both 01 and 10.
Hard Disk Requirements: An even number of hard disks with a minimum of four; maximum dependent on controller. All drives should be identical.
Array Capacity: (Size of Smallest Drive) * (Number of Drives ) / 2.
Storage Efficiency: If all drives are the same size, 50%.
Fault Tolerance: Very good for RAID 01; excellent for RAID 10.
Availability: Very good for RAID 01; excellent for RAID 10.
Degradation and Rebuilding: Relatively little for RAID 10; can be more substantial for RAID 01.
Random Read Performance: Very good to excellent.
Random Write Performance: Good to very good.
Sequential Read Performance: Very good to excellent.
Sequential Write Performance: Good to very good.
Cost: Relatively high due to large number of drives required and low storage efficiency (50%).
Special Considerations: Low storage efficiency limits potential array capacity.
Recommended Uses: Applications requiring both high performance and reliability and willing to sacrifice capacity to get them. This includes enterprise servers, moderate sized database systems and the like at the high end, but also individuals using larger IDE/ATA hard disks on the low end. Often used in place of RAID 1 or RAID 5 by those requiring higher performance; may be used instead of RAID 1 for applications requiring more capacity.
RAID partition manager
What will you do when system C drive or any other volume runs out of space, start from scratch? No, there is better choice, no matter you use RAID 10, RAID 01 or any other types of hardware RAID, you may use NIUBI Partition Editor to resize RAID volumes without reinstalling OS or losing data, everything keeps intact.
NIUBI Partition Editor is the most popular software in disk management field. It provides basic partition management to create, delete, format partition, change drive letter, etc. Advanced management to resize, move existing partition without data loss, copy, hide, set active, convert, defrag, check partition and much more.
- For Windows 10/8/7/Vista/XP (32 & 64 bit) user, download free partition software. (100% free, safe and clean).
- For Windows Server 2016/2012/2008/2003 (R2), download server partition software.
Watch the video how to resize RAID partition with free partition manager:
